MasterMsf 2 定制Metasploit Part 1
启程
鸡声茅店月,人迹板桥霜。
本章一开始写到:
One of the greatest challenges in life is being yourself in a world that’s trying to make you like everyone else.
Ruby基本知识
irb打开Interactive Ruby Shell。
# operator <<
a = "hello "
a << "world" # now a is "hello world"
b = a[0, 5] # now b is "hello"
c = a.split(" ") # now c is ["hello", "world"]
# to_s to_i
d = 55
e = d.to_s # e is "55"
f = e.to_i + 45 # f is 100
# hex dec
g = e.hex # g is 85; you can also use g = e.to_i(16)
h = (g + 15).to_s(16) # h is 0x64
# range
zero_to_nine = 0..9
i = zero_to_nine.include?(4) # i is true
j = zero_to_nine.min # j is 0
zero_to_nine.each{|zero_to_nine| print(zero_to_nine)} # that will print 0123456789
# method
def xorops(a, b)
res = a ^ b
return res
end
# boolean
k = 1 > 2 # so k is false; that is just similar to C++
def find_match(a)
if a =~ /Metasploit/ # regex, to find string which include "Metasploit"
return true
else
return false
end
end
# =~ is regex-matching
# s = "asdfasdfasd"
# s =~ /sdf/ will return the index 1
# s =~ /xxx/ will return nil
a = "123456789Metasploituidisdid"
bool_b = find_match(a) # bool_b is true
# for iteration
def for1(a)
for i in 0..a
print("Number #{i}\n")
end
end
for1(10)
# will print
# Number 0
# Number 1
# Number 2
# Number 3
# each
def each_example(a)
a.each do |i|
print(i.to_s + "\t")
end
end
a = Array.new(5) # a = [nil, nil, nil, nil, nil]
a = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
each_example(a)
# will print
# 10 20 30 40 50
# regex
n = "hell world"
r = /world/
r.match(n) # return #<MatchData "world">, which means matching succeeds
n =~ r # return the index
# you can combine your knowledge of regex with ruby
这个仓库有很多Ruby速查表。
在阅读源代码时,我们会经常遇到attr_accessor,例如在data_store.rb中的
attr_accessor :options
参考What is attr_accessor in Ruby?可以知道,其实它相当于两条语句:
attr_reader :options
attr_writer :options
它们等同于Java中对成员变量设置的get/set方法。所以attr_accessor实际上表明后面的成员变量是可读可写的。
深入解析Metasploit及其模块
Metasploit体系结构
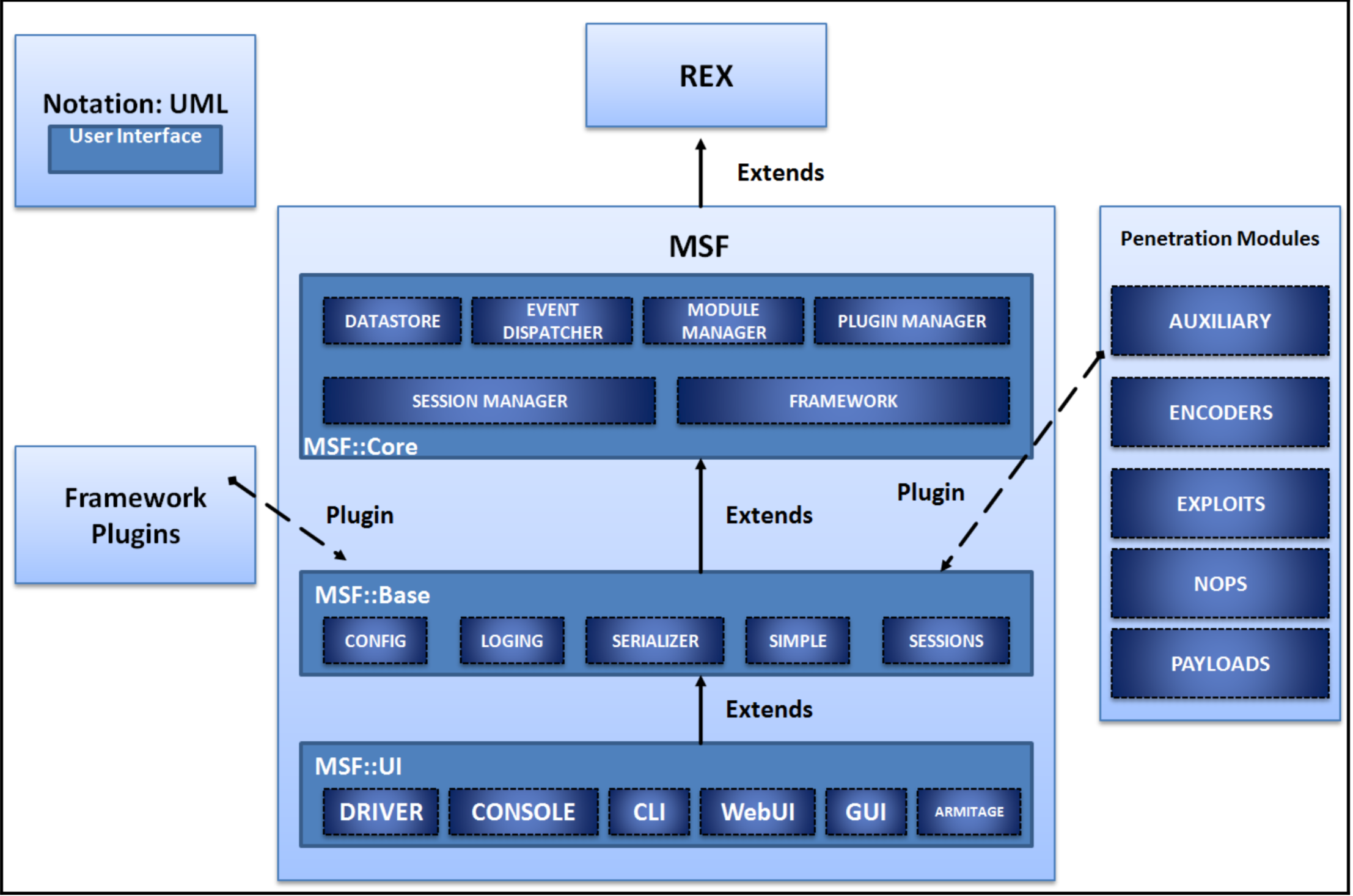
上图右侧即Metasploit中的5种模块。基本都已经接触过了。
基础库文件有三个:
- Ruby扩展(REX):处理几乎所有核心功能
- MSF核心:提供基本API和框架
- MSF基础:对模块提供友好的API
我们简单看一下Mac下的Metasploit文件格局:
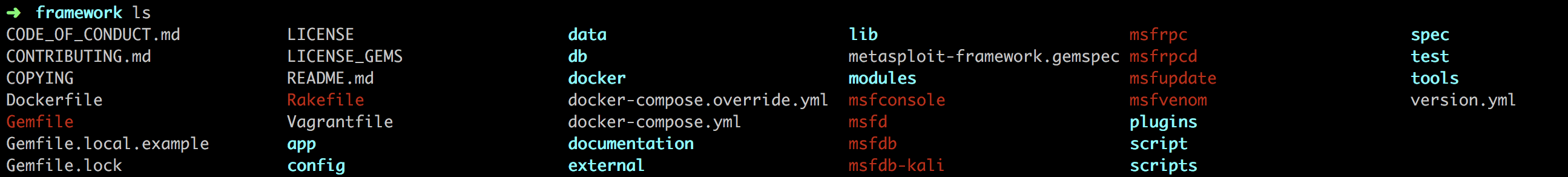
- lib 是Metasploit的核心

前面提到的三类基础库文件的路径:
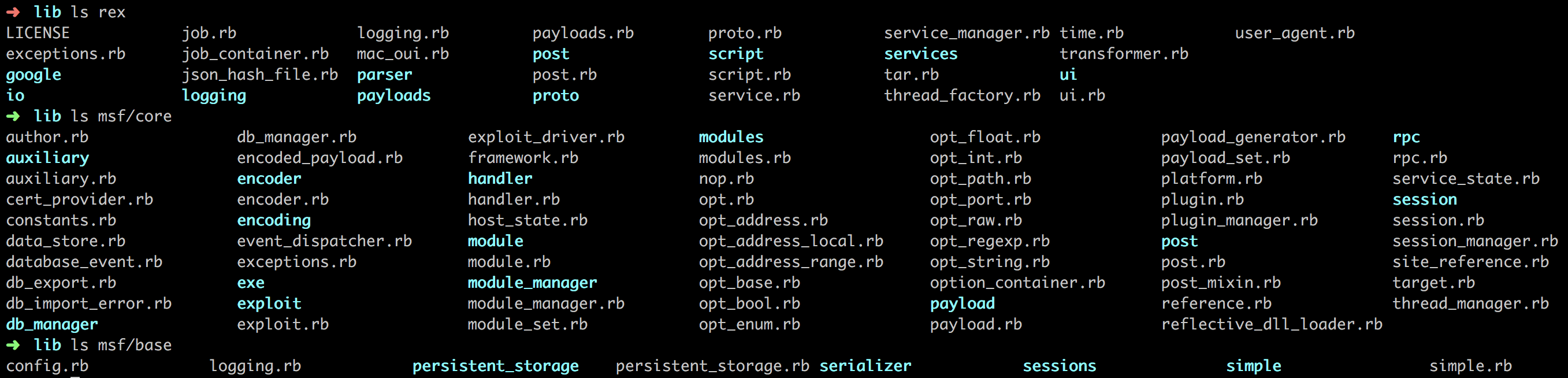
我们可以看到,在core下有按照前面提到的5类文件分类存放的目录。比如在core/exploits下有许多广泛使用的库文件:
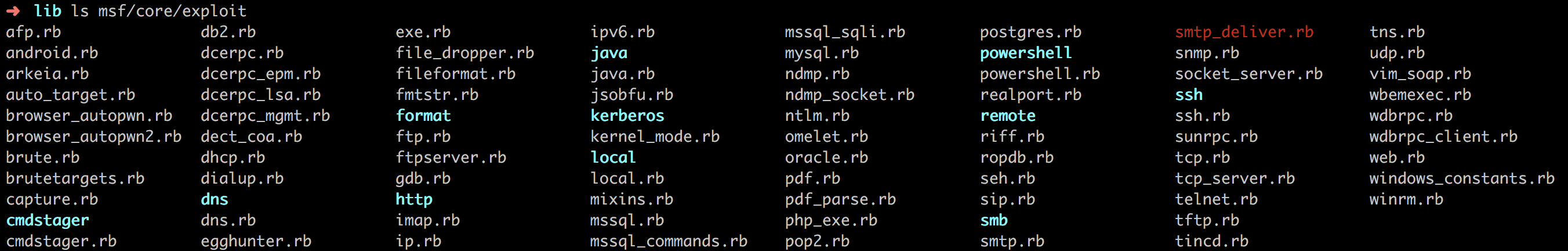
- modules 包含Metasploit的所有模块

- tools 包含由于辅助渗透测试的命令行程序,如查找jmp esp跳板地址的工具
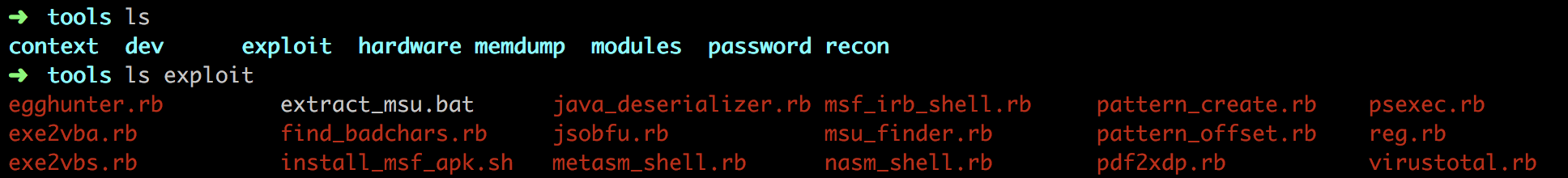
- plugins 包含所有扩展功能的插件,如OpenVAS、Nessus等可以使用load命令载入的工具

- scripts 包含meterpreter及其他脚本
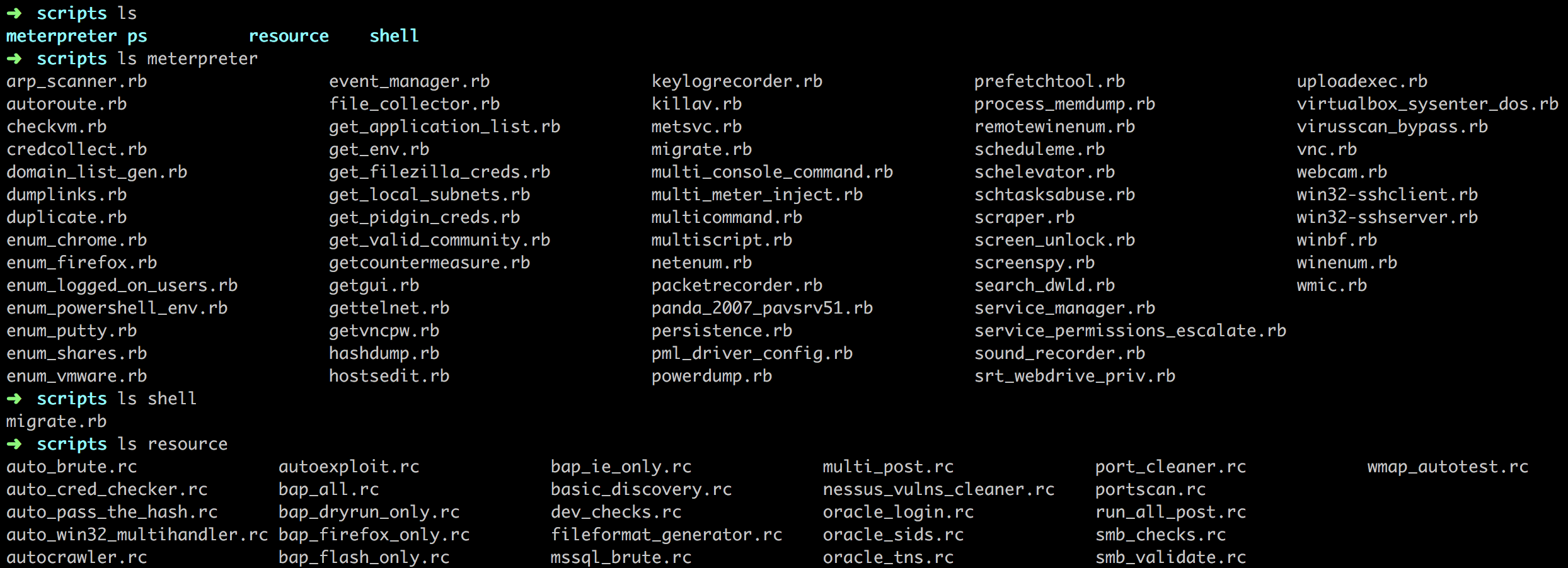
其中很多我们已经使用过。
示例模块
看个示例模块(在各个模块目录下都有对应的example.rb):
# modules/auxiliary/example.rb
class MetasploitModule < Msf::Auxiliary # 定义类的用途是辅助,`>`表示继承
def initialize(info = {})
super(
update_info(
info,
'Name' => 'Sample Auxiliary Module',
'Description' => 'Sample Auxiliary Module',
'Author' => ['Joe Module <joem@example.com>'],
'License' => MSF_LICENSE,
'Actions' => [
[ 'Default Action' ],
[ 'Another Action' ]
]
)
)
end
def run
print_status("Running the simple auxiliary module with action #{action.name}")
end
# auxiliary modules can register new commands, they all call cmd_* to
# dispatch them
def auxiliary_commands
{ "aux_extra_command" => "Run this auxiliary test commmand" }
end
def cmd_aux_extra_command(*args)
print_status("Running inside aux_extra_command(#{args.join(' ')})")
end
end
作者说开头要添加require 'msf/core',但貌似现在不需要了(是默认被导入吗)?自己编写模块还是加上吧。
辅助模块主函数是run方法,模块将从这里开始执行。
分析HTTP扫描器模块源码
modules/auxiliary/scanner/http/http_version.rb模块比较简单,我们看一下它的构成:
首先是模块说明、导入库文件、定义类的用途是辅助:
##
# This module requires Metasploit: https://metasploit.com/download
# Current source: https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework
##
require 'rex/proto/http'
class MetasploitModule < Msf::Auxiliary
require 'rex/proto/http'说明lib/rex/proto/http/下的所有文件(包含了各种http方法)都可以被当前模块使用:

接着调用渗透mixins类和扫描器mixins类:
# Exploit mixins should be called first
include Msf::Exploit::Remote::HttpClient
include Msf::Auxiliary::WmapScanServer
# Scanner mixin should be near last
include Msf::Auxiliary::Scanner
它们分别对应库文件:
- lib/msf/core/exploit/http/client.rb
This module provides methods for acting as an HTTP client when exploiting an HTTP server.
- lib/msf/core/auxiliary/wmapmodule.rb
This module provides methods for WMAP-enabled modules.
WMAP是一个基于Metasploit的通用Web应用程序扫描框架。
- lib/msf/core/auxiliary/scanner.rb
This module provides methods for scanning modules.
为理解上面的代码我们需要了解Ruby中的include和mixins机制,可以参考这篇文章。
Ruby 不直接支持多重继承,但是 Ruby 的模块(Module)有另一个神奇的功能。它几乎消除了多重继承的需要,提供了一种名为 mixin 的装置。
Ruby 没有真正实现多重继承机制,而是采用成为mixin技术作为替代品。将模块include到类定义中,模块中的方法就mix进了类中。
然后就是构造函数:
def initialize
super(
'Name' => 'HTTP Version Detection',
'Description' => 'Display version information about each system.',
'Author' => 'hdm',
'License' => MSF_LICENSE
)
register_wmap_options({
'OrderID' => 0,
'Require' => {},
})
end
最后是扫描:
# Fingerprint a single host
def run_host(ip)
begin
connect
res = send_request_raw({ 'uri' => '/', 'method' => 'GET' })
fp = http_fingerprint(:response => res)
print_good("#{ip}:#{rport} #{fp}") if fp
report_service(:host => rhost, :port => rport, :sname => (ssl ? 'https' : 'http'), :info => fp)
rescue ::Timeout::Error, ::Errno::EPIPE
ensure
disconnect
end
end
扫描器的思路很简单:发送一个GET请求,将返回结果进行指纹匹配。
run_host()将被scanner.rb调用:
# in lib/msf/core/auxiliary/scanner.rb
if (self.respond_to?('run_range'))
# No automated progress reporting or error handling for run_range
return run_range(datastore['RHOSTS'])
end
if (self.respond_to?('run_host'))
loop do
# Stop scanning if we hit a fatal error
break if has_fatal_errors?
# Spawn threads for each host
while (@tl.length < threads_max)
# Stop scanning if we hit a fatal error
break if has_fatal_errors?
ip = ar.next_ip
break if not ip
@tl << framework.threads.spawn("ScannerHost(#{self.refname})-#{ip}", false, ip.dup) do |tip|
targ = tip
nmod = self.replicant
nmod.datastore['RHOST'] = targ
begin
# run_host is invoked here
nmod.run_host(targ)
# ...
参考ruby-doc,上面的respond_to?是用来判断对象是否拥有某方法。毕竟run_host是我们开发者在自定义模块中设置的,所以扫描器模块还不知道用户是否定义了这个方法。
connect和send_request_raw帮助建立HTTP连接并发送请求:
# lib/msf/core/exploit/http/client.rb
#
# Connects to the server, creates a request, sends the request, reads the response
#
# Passes +opts+ through directly to Rex::Proto::Http::Client#request_raw.
#
def send_request_raw(opts={}, timeout = 20)
if datastore['HttpClientTimeout'] && datastore['HttpClientTimeout'] > 0
actual_timeout = datastore['HttpClientTimeout']
else
actual_timeout = opts[:timeout] || timeout
end
begin
c = connect(opts)
r = c.request_raw(opts)
# ...
如上,它将去调用rex/proto/http/client.rb中的request_raw来完成主要工作,它接受的参数如下:
# rex/proto/http/client.rb
#
# Create an arbitrary HTTP request
#
# @param opts [Hash]
# @option opts 'agent' [String] User-Agent header value
# @option opts 'connection' [String] Connection header value
# @option opts 'cookie' [String] Cookie header value
# @option opts 'data' [String] HTTP data (only useful with some methods, see rfc2616)
# @option opts 'encode' [Bool] URI encode the supplied URI, default: false
# @option opts 'headers' [Hash] HTTP headers, e.g. <code>{ "X-MyHeader" => "value" }</code>
# @option opts 'method' [String] HTTP method to use in the request, not limited to standard methods defined by rfc2616, default: GET
# @option opts 'proto' [String] protocol, default: HTTP
# @option opts 'query' [String] raw query string
# @option opts 'raw_headers' [Hash] HTTP headers
# @option opts 'uri' [String] the URI to request
# @option opts 'version' [String] version of the protocol, default: 1.1
# @option opts 'vhost' [String] Host header value
#
# @return [ClientRequest]
def request_raw(opts={})
opts = self.config.merge(opts)
opts['ssl'] = self.ssl
opts['cgi'] = false
opts['port'] = self.port
req = ClientRequest.new(opts)
end
rescue ::Timeout::Error, ::Errno::EPIPE用来处理超时异常。
我们来运行一下这个模块:
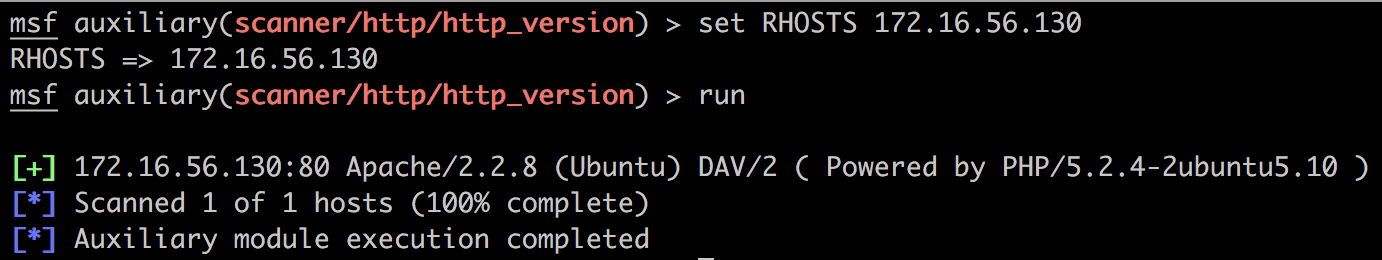
可以对应到run_host方法中的
print_good("#{ip}:#{rport} #{fp}") if fp
而report_service()
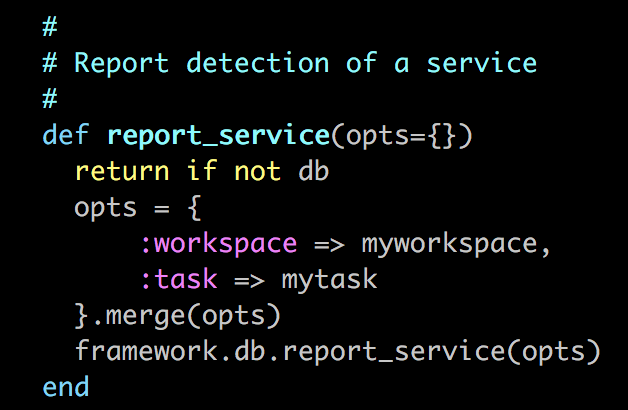
将把数据存储到数据库中,我们可以用services查看: